The healthcare sector has advanced technological innovation. But the fragmented way in which many hospitals acquire solutions can introduce cost, time, and resource inefficiencies that hinder care delivery and the ability to meet strategic objectives.
Therefore, the last several years have seen healthcare providers around the world embrace the concept of the 'smart hospital' as a means of optimizing multiple aspects of their IT performance.
However, hospital implementation of new technologies can present significant challenges for the adopting organizations in terms of cybersecurity, interoperability, and execution.
Smart Hospital Market Development
Therefore, the last several years have seen healthcare providers around the world embrace the concept of the 'smart hospital' as a means of optimizing multiple aspects of their IT performance.
However, hospital implementation of new technologies can present significant challenges for the adopting organizations in terms of cybersecurity, interoperability, and execution.
Smart Hospital Market Development
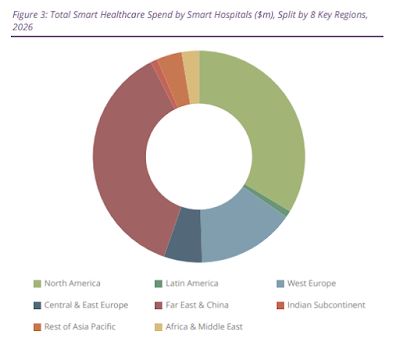
According to the latest worldwide market study by Juniper Research, smart hospitals will deploy 7.4 million connected Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices globally by 2026 -- that's estimated to be over 3,850 devices per smart hospital.
This global figure represents total growth of 231 percent over 2021 when 3.2 million devices were deployed. The concept of the IoMT involves healthcare providers leveraging connected devices such as remote monitoring sensors and surgical robotics to improve patient care, staff productivity, and operational efficiency.
The research identified smart hospitals in the U.S. and China as leading the global adoption of IoMT devices -- accounting for 21 percent and 41 percent of connected devices respectively, by 2026.
The research identified smart hospitals in the U.S. and China as leading the global adoption of IoMT devices -- accounting for 21 percent and 41 percent of connected devices respectively, by 2026.
Juniper analysts highlighted digital healthcare initiatives implemented during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and high levels of existing digitalization within healthcare infrastructure, as key to these nations' leading positions.
The new study findings identified remote monitoring as a key to delivering smart hospital services. It analyzed how the adoption of remote monitoring technologies accelerated during the pandemic significantly, due to difficulties associated with delivering in-person healthcare.
The new study findings identified remote monitoring as a key to delivering smart hospital services. It analyzed how the adoption of remote monitoring technologies accelerated during the pandemic significantly, due to difficulties associated with delivering in-person healthcare.
According to the Juniper assessment, this accelerated adoption is set to continue over the next five years, as hospital patients become acclimatized to remote monitoring and benefit from proactively managing and treating health conditions.
However, the analysts identified that the real-time nature of remote monitoring requires low latency, high bandwidth connections to ensure the transmission of patients' health data is not interrupted or distorted.
However, the analysts identified that the real-time nature of remote monitoring requires low latency, high bandwidth connections to ensure the transmission of patients' health data is not interrupted or distorted.
As a result, Juniper encourages smart hospital vendors to develop partnerships with network operators to leverage multi-access edge computing to drive major reductions in lag and latency.
Outlook for Smart Hospital IoMT Applications Growth
"The emergence of remote monitoring within healthcare presents an opportunity for network operators to place themselves within the digital healthcare value chain," said Adam Wears, research analyst at Juniper Research. "Smart hospital technologies generate significant quantities of data, meaning that the edge computing function provided by network operators will be crucial to the successful roll-out of these systems."
"The emergence of remote monitoring within healthcare presents an opportunity for network operators to place themselves within the digital healthcare value chain," said Adam Wears, research analyst at Juniper Research. "Smart hospital technologies generate significant quantities of data, meaning that the edge computing function provided by network operators will be crucial to the successful roll-out of these systems."
That said, I anticipate digital healthcare initiatives will gain new momentum this year as more hospital executive leaders task their CIO to explore proof of concept (PoC) deployments of promising IoMT use cases and associated edge computing applications.
As the number of deployed devices continues to grow, demand for unified endpoint management (UEM) solutions will increase. Securing IoMT connected devices within a hospital environment and remote monitoring at patient homes will require developing new IT security compliance best practices.