Precision Medicine uses molecular info to extract the optimum medical method from diagnostic protocols, by merging the impact of environmental and genetic factors. Data access is essential, with genetic metabolic and clinical data used to build a fuller picture of a patient's biology.
Moreover, the primary aim of precision medicine is to design and optimize a pathway for diagnosis, therapeutic intervention, and prognosis, using large biological datasets.
Personalized, evidence-based medicine uses stored health data, which includes patient diagnosis, laboratory work, insurance claims, and demographic information. The results enable healthcare providers to predict and prevent some illnesses.
Precision Medicine Market Development
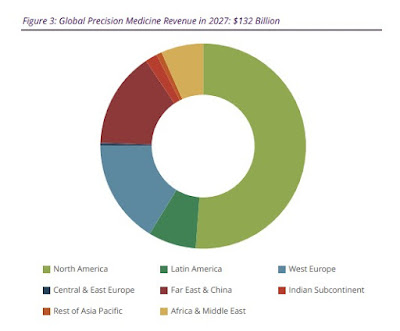
According to the latest worldwide market study by Juniper Research, the total investment in precision medicine will reach $132.3 billion globally by 2027 -- that's increasing from only $35.7 billion in 2022.
The significant market growth of 270 percent is a result of emerging technologies and infrastructure -- such as artificial intelligence (AI) -- which aids precision medicine by predicting risks for certain diseases.
These technological advancements, combined with the healthcare sector’s need to increase efficiencies in the face of a potential economic downturn, will encourage healthcare providers to invest further in precision medicine.
According to the Juniper assessment, precision medicine leverages advances in personal genomics to enable healthcare providers to prepare preventative plans and disease treatments based on gene variability.
Reductions in adverse reactions from ineffective medication, improving the efficacy of treatment plans via personalization, and cutting patient spending on medication, will be the primary drivers of precision medicine adoption among healthcare providers.
To maximize these medical benefits, Juniper analysts identified the use of AI to ingest and process large amounts of healthcare data to increase the future accuracy of medical diagnoses.
"The rapid increase in accuracy, as systems become more advanced, will create a virtuous cycle of continuous improvement; catalyzing further growth and adoption of precision medicine in healthcare sectors over the next 5 years," said Cara Malone, research analyst at Juniper Research.
The latest research finding identified that the most significant public policy issue surrounding precision medicine will likely arise from patient data privacy concerns. In particular, if and when a person's genetic data is stored and shared without permission.
In many countries, but predominantly in the U.S. market, there is suspicion that uncovering genetic predispositions using precision medicine could lead to medical insurance providers leveraging these insights to increase healthcare premiums.
Outlook for Regional Growth of Precision Medicine
To allay these concerns, all medical technology vendors must consider voluntarily adopting strong codes of conduct around data privacy, as well as creating independent advisory councils, to reassure people and limit the scope of data sharing.
That said, I believe personal genetic data privacy will become of paramount importance across the globe, as more national and international government bodies create medical data governance policies that regulate this emerging sector of the Global Networked Economy.