Digital identity verification is a security method applied in the processing of digital transactions. Digital identity verification is used to enable the remote verification of an individual’s identity, ensuring that they are who they claim to be online.
This is most often used for digital onboarding customers onto an online service, but can also be used to verify identity when authorizing Fintech money transfers, or for access management.
With the growing threats and increasingly complex fraud methods used by malicious actors, it is vital that institutions that handle sensitive data use up-to-date methods to protect their end-users.
Digital Identity Market Development
Many digital identity verification vendors offer solutions that increase the accuracy, security, and user experience of the digital onboarding process, and of other digital identity verification use cases.
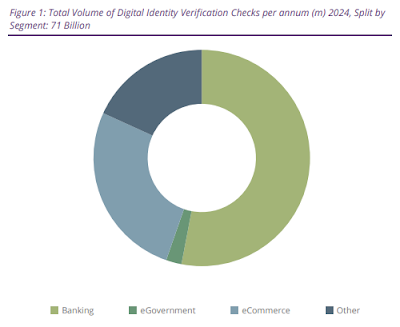
It's important that due to the variety of digital business use cases, other secure forms of identity verification will gain traction.
According to the latest worldwide market study by Juniper Research, the implementation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in identity verification will reduce the average time spent per digital onboarding check from over 11 minutes in 2023, to under 8 minutes in 2028.
As AI-based solutions become increasingly accurate, they reduce the number of identity checks referred to a human agent for review, and the need for ID photos to be retaken.
This decreases the time required for each verification, as well as the associated costs. The use of AI will also play a key role in protecting against emerging threats, such as synthetic identity fraud.
Juniper's analysts anticipate that the widespread adoption of digital verification within banking, particularly mobile banking, will continue to drive digital onboarding revenue growth.
Despite the proven increase in efficiency reducing the cost of each individual digital identity verification check, the growing volume of checks, particularly in developing regions, will offset this progress.
As such, Juniper Research now forecasts that total spending for banks will increase from $7.4 billion in 2023 to $9.9 billion in 2028 -- that's representing a 34 percent increase in investment.
"Growth will be particularly strong in developing markets, where rising smartphone penetration is making mobile banking more readily available; driving growth in digital onboarding," said Michael Greenwood, research analyst at Juniper Research.
Outlook for Digital Identity Applications Growth
To capitalize on this, digital verification vendors must develop onboarding processes that emphasize checks other than credit scores, such as mobile operator history, in order to maximize viability in emerging regions.
That said, I believe the popularity of digital-only banks is driving this application growth, as these providers are reliant on digital identity verification checks. Also driving growth are banks and other legacy financial service firms that will follow the Fintech leaders.
In the U.S. government market, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides a framework for digital identity and acts as a body for verification standards, also recognized globally.