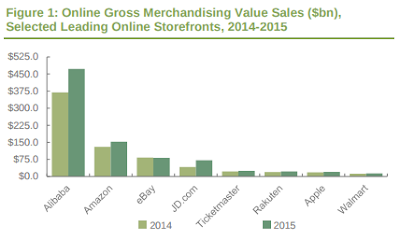
Online retailers have been a source of disruption for many incumbents around the globe. Over the past decade, eRetail adoption has accelerated and in 2015 online payments for physical goods totaled $1.66 trillion, while sales of digital goods and services generated a additional $754 billion.
Credit and debit card payments have been the primary payment method in the online arena. There are now about 9.5 billion credit and debit cards in circulation worldwide. Moreover, the dominance of the leading payment card provider is reinforced by the fact that online retailers typically prefer these cards.
Meanwhile, there's been an important shift in the market. In the past, the smartphone was used as a means of discovery, but not purchase of products and services. Now, the smartphone is used for both product discovery as well as the actual purchase. New technologies are enabling this shift.
eRetail Market Development Trends
According to the latest market study by Juniper Research, the integration of technologies such as bots and natural language interfaces will lead to remote goods purchases by mobile totaling $2.1 trillion by 2021. That growth represents a 100 percent increase from the anticipated spend on physical and digital goods in 2016.
Juniper analysts believe that rising smartphone use in digital retail was the underlying cause for stakeholder development in the following areas: bots, natural language processing, disruption at the payment gateway, and understanding shopper intent through conversation.
The Juniper study found that shoppers would likely abandon online experiences where keyword search and menu-driven website navigation systems were in place. It suggested that where merchants deployed conversational interfaces -- such as bots and natural language search -- they would be able to meet the consumer needs.
The North Face, for example, has developed an intelligent digital assistant to help consumers choose the appropriate product on their retail website. Meanwhile, Facebook, Google and online retailers such as Etsy are investing heavily in similar real-time analytics to transform the online retail experience.
"Product search and discovery is a key stage in the shopper journey," said Steffen Sorrell, senior analyst at Juniper Research. "Offering a conversational consumer interface, then marrying intent with contextual product data will drive merchant differentiation."
Outlook for Online Payment Innovation
Additionally, the study revealed that substantial activity is taking place to improve the consumer experience at the point of payment. Disruptive players are simplifying the online shopper's journey by re-engineering the checkout process.
Klarna, the Swedish eCommerce company, avoids using card number entry or usernames and passwords. Instead, online retail shoppers can enter more basic identification information, such as their email address and postcode.
Meanwhile, cognitive computing and machine learning is being used to minimize the chance of payment rejection. Adyen, for example, are applying the new technology to avoid payment rejection due to bad formatting or mis-routed connections to the acquiring bank.
Credit and debit card payments have been the primary payment method in the online arena. There are now about 9.5 billion credit and debit cards in circulation worldwide. Moreover, the dominance of the leading payment card provider is reinforced by the fact that online retailers typically prefer these cards.
Meanwhile, there's been an important shift in the market. In the past, the smartphone was used as a means of discovery, but not purchase of products and services. Now, the smartphone is used for both product discovery as well as the actual purchase. New technologies are enabling this shift.
eRetail Market Development Trends
According to the latest market study by Juniper Research, the integration of technologies such as bots and natural language interfaces will lead to remote goods purchases by mobile totaling $2.1 trillion by 2021. That growth represents a 100 percent increase from the anticipated spend on physical and digital goods in 2016.
Juniper analysts believe that rising smartphone use in digital retail was the underlying cause for stakeholder development in the following areas: bots, natural language processing, disruption at the payment gateway, and understanding shopper intent through conversation.
The Juniper study found that shoppers would likely abandon online experiences where keyword search and menu-driven website navigation systems were in place. It suggested that where merchants deployed conversational interfaces -- such as bots and natural language search -- they would be able to meet the consumer needs.
The North Face, for example, has developed an intelligent digital assistant to help consumers choose the appropriate product on their retail website. Meanwhile, Facebook, Google and online retailers such as Etsy are investing heavily in similar real-time analytics to transform the online retail experience.
"Product search and discovery is a key stage in the shopper journey," said Steffen Sorrell, senior analyst at Juniper Research. "Offering a conversational consumer interface, then marrying intent with contextual product data will drive merchant differentiation."
Outlook for Online Payment Innovation
Additionally, the study revealed that substantial activity is taking place to improve the consumer experience at the point of payment. Disruptive players are simplifying the online shopper's journey by re-engineering the checkout process.
Klarna, the Swedish eCommerce company, avoids using card number entry or usernames and passwords. Instead, online retail shoppers can enter more basic identification information, such as their email address and postcode.
Meanwhile, cognitive computing and machine learning is being used to minimize the chance of payment rejection. Adyen, for example, are applying the new technology to avoid payment rejection due to bad formatting or mis-routed connections to the acquiring bank.