Although the rise of electronic commerce has slowed somewhat since the initial explosive growth, the overall volume and value of eCommerce transactions continue to climb. There are several drivers supporting this growth. A key driver is the international adoption of a Global Networked Economy.
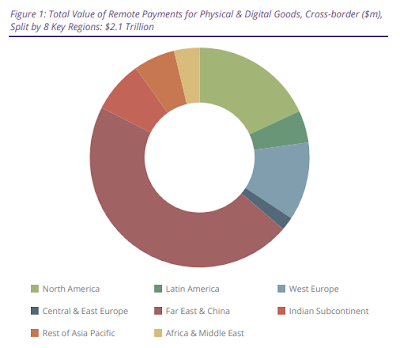
According to the latest worldwide market study by Juniper Research, the value of international cross-border eCommerce is forecast to exceed $2.1 trillion in 2023 -- that's up from $1.9 trillion in 2022.
International eCommerce Market Development
This growth of over 13 percent in a single year reflects the increasing success of online marketplaces that offer goods across borders, as well as the rising viability of cross-border sales as an eCommerce model.
The new research study found that as eCommerce models diversify -- including models such as buy now pay later and click and collect -- cross-border options must also keep pace, by enabling local distribution and payment partnerships.
Juniper research analysts recommend that cross-border vendors and service providers offer localized eCommerce models, or they will lose out to options that better serve consumer appetites.
The research also uncovered that the online marketplace model, where large vendors, such as Amazon or Wish.com, sell goods to users on behalf of cross-border product suppliers, will be critical to growth.
This model represents an easy way to access a large audience of online consumer buyers while ensuring that accepting payments and other logistical issues are handled in a satisfactory manner.
"The marketplace model within eCommerce takes the complexity away, meaning that cross-border merchants can provide a localized service," said Nick Maynard, head of research at Juniper Research.
As such, online marketplaces are an excellent way to gain immediate access to an existing user base, albeit one that can be restrictive compared with having a direct-to-consumer relationship.
The global market study found that physical goods will account for over 97 percent of cross-border eCommerce spending in 2023, with digital goods making up the remainder of the forecast growth.
Outlook for Cross-Border eCommerce Applications Growth
Juniper's analysts identified the maturity of the cross‑border export of physical goods business model as a major factor in this difference, as well as increasingly cost‑conscious key stakeholders.
Juniper recommends that online payments vendors support a wide range of complementary local payment methods, in order to capitalize on this sizeable market opportunity.
That said, given the evolution of consumer shopping habits, I believe progressive retailers will continue to rely on their online stores -- the global COVID-19 pandemic made the necessity of having an online presence abundantly clear for many retailers.
Those merchants without a developed online presence and automated shopping capability were left at a significant disadvantage. That's because the convergence of in-store and digital commerce is clearly driving new applications and associated global market opportunities.