Mobility as a Service (MaaS) is a rapidly growing transportation offering where people are able to plan, book, and pay for a variety of service types, through a joint digital commerce channel.
It is a shift away from expensive personally owned modes of transportation, such as automobiles, towards a low-cost subscription or pay-as-you-go services.
It is achieved through the combination of public transport -- such as trains and buses -- as well as private transport, and micro-mobility, including bikes and scooters, to get users from one destination to another.
Mobility as a Service Market Development
Mobility as a Service users are able to pay for the service provided either on a monthly basis or pay per trip.
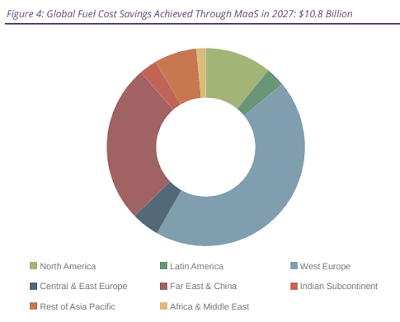
According to the latest worldwide market study by Juniper Research, Mobility as a Service will generate fuel cost savings of $10.8 billion by 2027 globally -- that's increasing from $2.8 billion in 2022, a growth of 282 percent.
Juniper Research anticipates these savings will be achieved by the service's ability to reduce congestion by displacing private vehicle usage with public transport over new MaaS platforms.
MaaS platforms provide consumer urban transit solutions -- such as ride-hailing, bus, and metro trains, integrated into a single digital commerce app.
The research findings uncovered that more consumers will likely turn to MaaS solutions, as fuel costs increase globally. The cost of gasoline has become increasingly volatile as producers manipulate supply.
The latest Juniper survey found that 41 percent of respondents ranked the cost of transport as being the most important factor when it comes to selecting a method of transportation.
MaaS growth is due to the perception of being a less-expensive travel alternative. MaaS adoption is also due to the convenience it provides by offering transportation with planning, purchasing, and ticketing combined in a single software app.
Furthermore, Juniper analysts predict that CO2 reduction from private car journeys displaced is also fuelling the growth of MaaS applications.
"MaaS has the ability to improve corporate social responsibility, as a result, MaaS vendors must appeal to companies by demonstrating how MaaS can significantly reduce their carbon emissions from travel," said Cara Malone, research analyst at
Juniper Research.
Outlook for Micro-Mobility App Usage Growth
The distance traveled via micro-mobility options -- described as a form of transportation using lightweight vehicles such as bicycles and scooters -- is set to grow 780 percent globally between 2022 and 2027.
Micro-mobility enables service users to traverse through highly congested cities for the first and last mile of their journey. The growth will be driven by the increased deployment of micro-mobility infrastructure, including docking stations, bicycles, and scooters.
That said, across the globe, many smartphone users already have one or more micro-mobility apps on their mobile devices. Moreover, micro-mobility service saturation became a significant issue in some urban markets, and local government leaders responded with increased regulation. Regardless, the outlook for new growth in this space is promising.